How Brazilian propolis prevents metabolic disorders
07/09/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
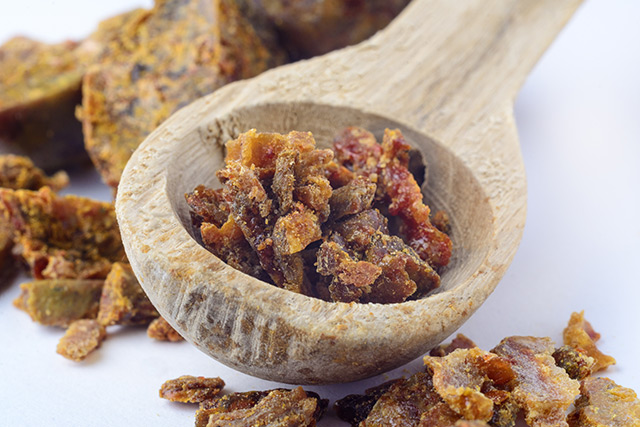

A study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine has found how Brazilian propolis prevents metabolic disorders, such as Type 2 diabetes. Researchers at Rakuno Gakuen University, Aichi Gakuin University, and Asahikawa Medical University aimed to distinguish the immunosuppressive cells directly elicited by propolis extract. They also sought to assess the flavonoids that induce such cells.
- For the study, they injected a dose of 100 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) ethanol extract of Brazilian propolis to lean and high fat-fed obese mice twice a week for one month.
- Then, they used flow cytometry (FACS) analysis to monitor immune cells in visceral adipose tissue and the peritoneal cavity.
- Brazilian propolis ethanol extract and its constituent compounds were also administered in isolated macrophages and macrophage-like cells. The team then investigated the expression of immune suppressive myeloid markers. M1 macrophages produce pro-inflammatory cells, contributing to fat inflammation.
- In addition, the obese mice received kaempferol, one of the identified compounds of the Brazilian propolis. Then, the team conducted a FACS analysis on fat.
- In vivo results revealed that the treatment of Brazilian propolis ethanol extract induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the visceral adipose tissue and the peritoneal cavity of both lean and obese mice. This suggested that the treatment can potentially prevent both the onset and progression of type 2 diabetes.
- In vitro results showed that Brazilian propolis ethanol extract directly stimulated cultured M1 macrophages to turn into MDSCs.
- The treatment of kaempferol also led to the accumulation of MDSCs in the visceral adipose tissue of mice.
In conclusion, the promotion of MDSCs in visceral adipose tissue brought by the Brazilian propolis ethanol extract and kaempferol can potentially be used for anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory treatments.
For the full text of the study, visit this link.
Journal Reference:
Kitamura H, Saito N, Fujimoto J, Nakashima K, Fujikura D. BRAZILIAN PROPOLIS ETHANOL EXTRACT AND ITS COMPONENT KAEMPFEROL INDUCE MYELOID-DERIVED SUPPRESSOR CELLS FROM MACROPHAGES OF MICE IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2018; 18(138). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2198-5
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, bees, Brazilian propolis, chronic inflammation, diabetes, diabetes prevention, kaempferol, metaboic disorder prevention, metabolic disorders, metabolic syndrome, metabolism, natural cures, natural prevention, Propolis, Type 2 Diabetes