Zinc is an effective treatment for coronavirus infection, blocks viral replication
06/10/2020 / By Lance D Johnson

The health officials who led the federal coronavirus task force enjoyed plenty of opportunities to educate Americans on how to face and overcome severe acute respiratory syndrome. However, these “infectious disease experts” mentioned next to nothing about how to equip the individual immune system, how to prevent viral attachment, lessen viral load, and block viral replication. Americans were kept in the dark and left with limited, unsustainable options – like avoiding human contact and staying in a state of isolation into perpetuity.
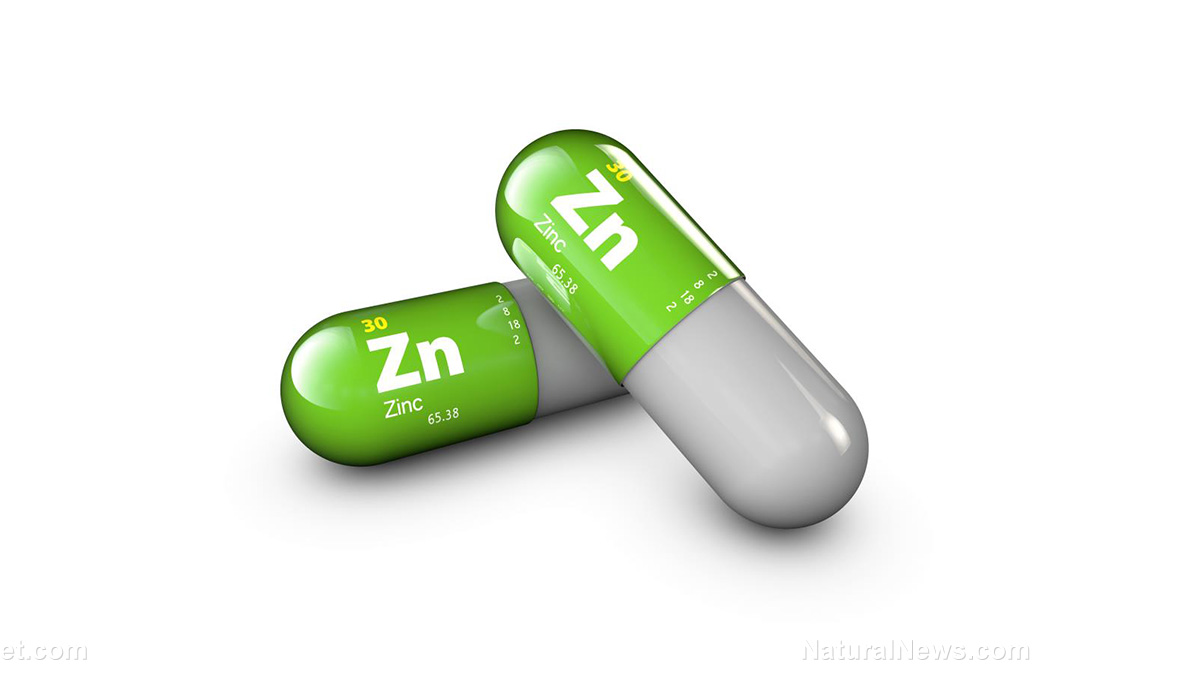
Now there’s ample evidence that a common mineral, zinc, can block the replication of the virus behind the covid-19 dilemma.
Zinc inhibits coronavirus, blocking viral replication in cells
RNA viruses, including poliovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, picornaviruses, influenza virus, and coronavirus can all be stopped at the cellular level by increasing the intracellular concentration of zinc. Medical researchers from the Molecular Virology Laboratory, Department of Medical Microbiology, Center of Infectious Diseases, Leiden University Medical Center, in the Netherlands explain that the replication of all these viruses can be stopped when zinc concentrations force a correction of proteolytic processing of viral polyproteins.
Using electromobility shift assays (EMSA) in the presence and absence of Zn2+, the researchers measured the binding affinity of the viral RNA and measured a 3-4 fold reduction in RNA-dependent RNA polymerase binding in the presence of zinc. By using zinc ionophores like pyrithione, the researchers proved that increased intracellular zinc impairs the replication of RNA viruses, severely inhibiting the replication of equine arteritis virus (EAV) and SARS-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in cells. The two viruses share a core enzyme needed for multi-protein replication that is easy to block using zinc. The researchers didn’t even need to rely on pyrithione to transport zinc across the plasma membrane because zinc could effectively inhibit RNA synthesizing activity in a direct manner. Because of this, the in vitro activity of both viruses polymerases could be blocked with ease. Moreover, zinc was found to specifically block the initiation step of RNA synthesis, inhibiting the elongation and template binding of SARS-CoV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. The researchers also showed that the absence of zinc, through chelation of the mineral from cells, reverses its therapeutic effect, allowing viral replication to continue.
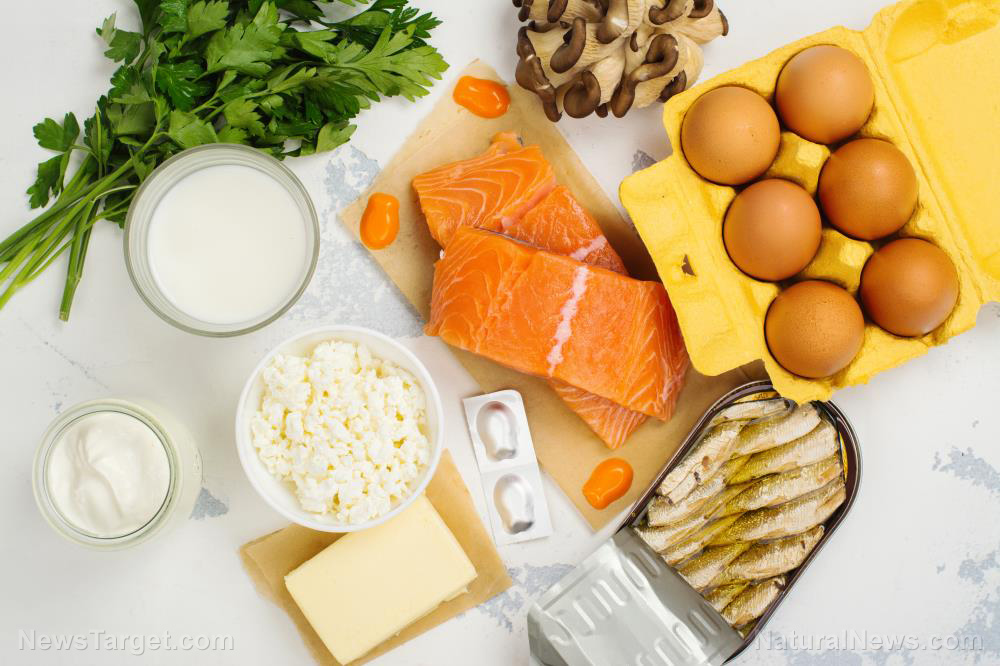
Zinc is therapeutic medicine against many types of viruses and bacteria
Zinc has a history of therapeutic use against viruses and bacteria, strengthening the human immune response. Why aren’t public health systems making this the primary focus – enhancing the intracellular immune response? During the covid-19 dilemma, strengthening the innate immune response has not been encouraged and the public has been kept ignorant and afraid. Healthcare systems are relying heavily on ventilators, and ventilator-associated lung damage and ventilator-associated pneumonia have become a serious issue that costs lives. Many healthcare systems have relied on fraudulent data that discouraged the use of known antiviral medicines. The therapeutic efficiency of chloroquine, for example, acts as a zinc ionophore, allowing for enhanced zinc absorption into the cells. Combined with a zinc supplement, this combination can inhibit SARS-CoV RNA polymerase and decrease activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, which is a known receptor for SARS-CoV-2.
The antiviral properties of zinc can also convey an up-regulation of interferon production, allowing the innate immune system to more rapidly respond to a virus and eliminate an infection from the body. Furthermore, zinc possesses anti-inflammatory activity and allows T-cell immune function to work efficiently, limiting cytokine storms that are observed in severe cases of covid-19.
As zinc absorption is increased in the cells, the risk of bacterial co-infection is lowered, warding off other infectious that may try to take hold of an overworked immune system, such as pneumonia. (Zinc exhibits a direct antibacterial effect toward S. pneumoniae.) Through this mechanism, zinc is also responsible for clearing the mucous from the body and improving the barrier function of the respiratory epithelium. The many people who suffered and died from covid-19 infections were mostly in high risk categories where zinc deficiency is often observed. Obesity, diabetes, and atherosclerosis are all known risk groups for zinc deficiency and have been the most common underlying conditions that have led to covid-19 deaths.
For more on the therapeutic effect of nutrition for infectious disease, check out Nutrients.News.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, chloroquine, co-infections, innate immune response, polymerase activity, research, RNA synthesis, T-cell function, viral load, viral replication, virus receptors, zinc, zinc deficiency, zinc ionophore
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 SUPPLEMENTS REPORT